If you’re looking for a simple connection between your software and Planpoint, you can look into our API.
Getting Started
In your React project, begin by importing all components of Planpoint SDK:Planpoint Views
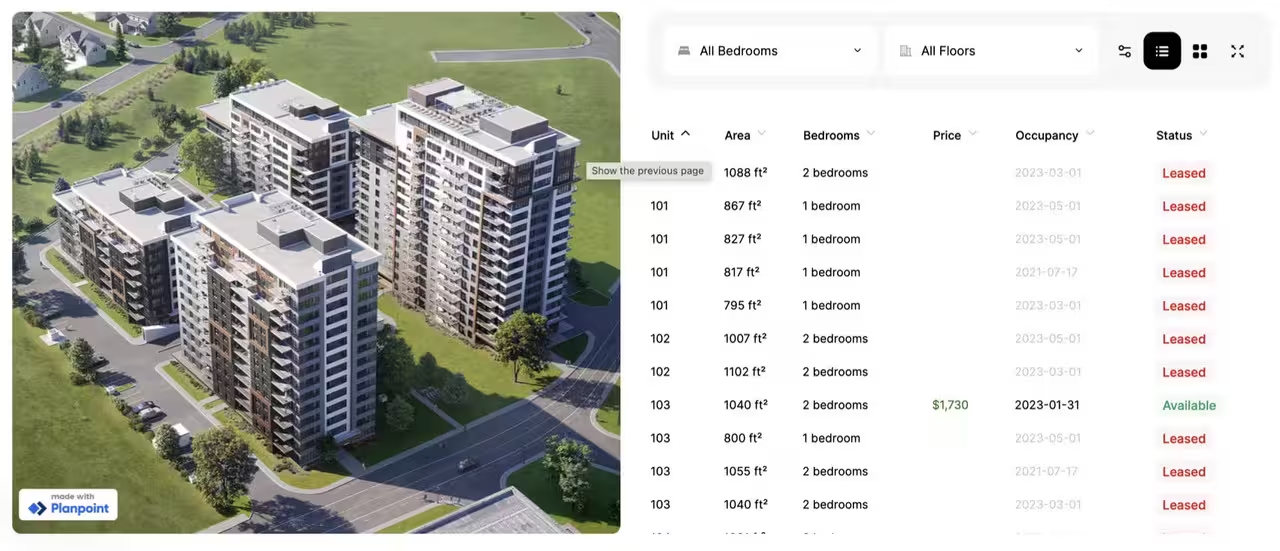
The Plainpoint SDK provides a set of views ready to integrate to your websites. Plainpoint will serve ready-to-use graphical components, while handling all processing and data management. There are four core views which can be rendered via the SDK. Let’s have a look at them and their corresponding integrations. 1. Project View The project view provides a list of current projects with relevant data, including the area, occupancy, price, and others. Integrating the project view in your project requires the ID of a project that has previously been configured in the dashboard. Loading a project looks like this:

- action events correspond to unit actions in the form of buttons above the unit gallery.
- shortlist events correspond to interactions with the shortlist feature in the top right corner.
Event Management
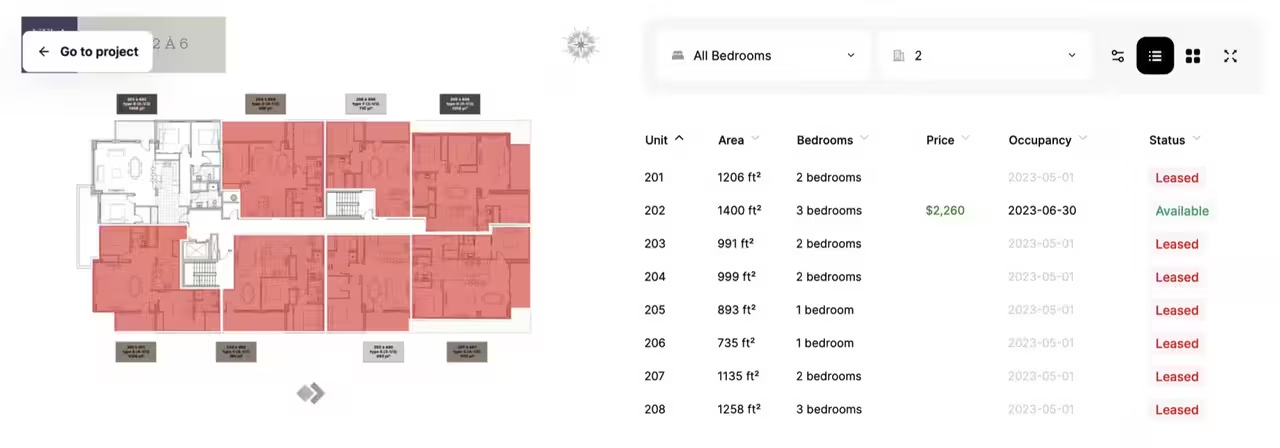
Each view rendered with the SDK provides a unique list of events and triggers. You can pass a listener configuration to each component from planpoint-sdk/core to listen for and respond to said events. Project views provide different kinds of events:- stage events will listen to events across the image displayed on the right. There’s a hover and click event for the floors displayed on the project. Each event will carry the id of the floor in scope.
- filter events will fire whenever users click any of the available filter dropdowns along with filters hidden in the filter menu. Each filter event will carry the name of the filter, the previous value as well as the new value.
- view events will fire whenever users toggle full screen, grid or list view. Each event will carry the name of the previous and current view.
- entity events will fire whenever users hover over or click any of the entities listed in the table on the right of the screen. Each event will carry the id of the entity in scope.